
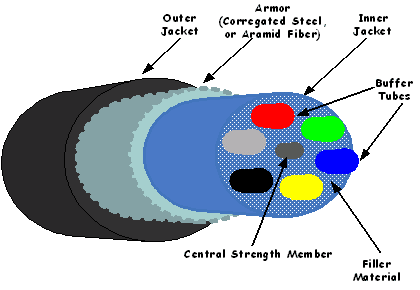

An optical cable is an optical fiber that has been coated with a tough layer of resin. This layer is then surrounded by what is referred to as a jacket layer. Most often, the jacket layer of the optical cable is made of plastic. The layers around the optical fiber help provide the optical cable with extra strength. At the same time, these layers do not prevent the fiber within the optical cable from maintaining its properties.
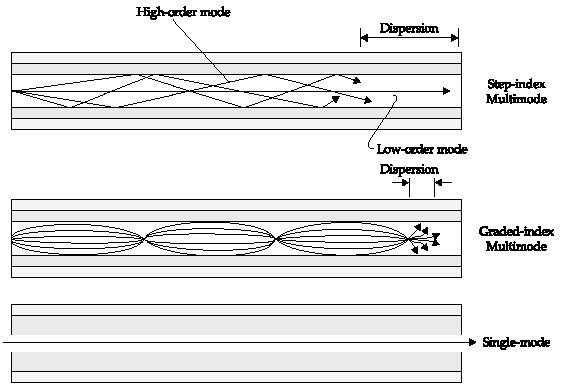
The fiber in an optical cable is typically made of either glass or plastic. The fiber itself is thin and transparent, making it capable of transmitting light. An optical cable may have thousands of these fibers within it, making the cable capable of transmitting a great deal of information through bandwidth communication or large amounts of electricity when the optical cable is used for this purpose.
An optical cable can be purchased with a wide variety of different sheathings and armor. The intended use for the optical cable determines which type should be selected. Uses can range from use as power lines, burial in trenches, attaching to aerial telephone poles, use in conduit, submarine installation, and placement within paved streets.
When used indoors, the jacketed fiber of the optical cable is usually enclosed and uses a lightweight plastic cover. Each end of the optical cable is usually terminated with an optical fiber connector, which makes it easier to connect and disconnect the optical cable. If the optical cable is to be used outdoors, a loose-tube construction design is usually used. This design consists of semi-rigid tubes that make it possible for the outside of the optical cable to stretch without stretching the fiber inside. This keeps the fiber protected from tension and extreme changes in temperature.
The fiber within the optical cable also needs to be protected from water. This is because the hydrogen and the hydroxyl ions within water will diffuse into the fiber. If this occurs, the strength of the fiber is reduced. Copper tubes or special water-repellent jellies are used to keep water out of the optical cable and away from the fiber.

